Facial Injury Among Travelers in Bali – Injury, particularly road traffic accident-related injury, was the leading cause of mortality among foreign travelers globally. More than a million people are estimated to have died or been disabled as a result of an accident. The most prevalent injury in the field of plastic surgery sector among overseas travelers was a facial fracture or facial injury.
Facial Injury in Bali
Facial injury represents a typical traumatic event that affects both functional and cosmetic elements. Due to cultural, social, as well as environmental variables, the causes and prevalence differ by country. There has been little study on face injuries among international visitors in Bali, a famous tourist destination.
The purpose of this article is to clear up the epidemiologic situation of facial injuries involving foreigners in Bali, to provide a thorough knowledge of patterns and demographics, and to guide the creation of preventative and management initiatives.
Cases Study in Bali for Facial Injury
A research investigation of 126 facial injury cases discovered that most of them were males between the ages of 16 and 30. The leading cause, which accounted for 38.1% of all occurrences, was motor vehicle accidents (MVA).
The majority of the individuals arrived with head wounds and got first treatment in 12 hours. The 16 to 30 age group had the greatest rate of face fractures, resulting in 52.4% of all occurrences. The causes varied, with falls as the second most prevalent. The majority of patients got their first medical intervention in 12 hours, with others obtaining treatment between 24-24, 24-36, and 36-48 hours.
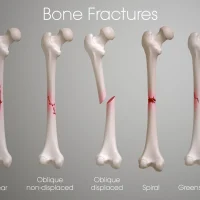
According to certain research, 46.8% of patients in some facilities required surgery, with head injuries being the most prevalent. The nasal area had the most fractures, followed by the craniofacial, maxillofacial, as well as mandibulofacial regions. Orbital as well as zygoma fractures constituted the most prevalent types of fractures. The majority of nasal bone fractures were without septal deviation, but around 60% of mandibulofacial fractures comprised multiple fractures that involved the ramus of the mandible.
Confronting The Challenge Among Travelers
As a result of their intricate and overlapping anatomical systems, as well as their influence on function and esthetic looks, facial fractures provide the biggest challenge in their care. It is really concerning when their pattern varies substantially in different parts of the planet. Different patterns of face fractures come from differences in the mechanism and source of damage.
The results showed no significant variation in the main demographic features revealed in our study when compared with an identical investigation conducted in other countries. Males suffered greater injuries. This may be related to the fact that males are more likely to engage in personal violence, drug usage, accidents, and so on as a result of their engagement within the productive population.
Nevertheless, the ratio of males to girls in our research, which is 2.4:1, differs dramatically from that observed in other previously published reviews, which revealed a greater ratio. This might be owing to the same number of both male and female visitors to Bali.
The study discovered a low prevalence of face fractures in young individuals aged 16-30, which it ascribed to their aggressive character and irresponsible driving. However, as they become older, the number of them reduces. Because of their protective surroundings and specific anatomical characteristics, children under the age of 16 have a reduced incidence. This low prevalence is also seen among elderly people, who spend a lesser amount of time driving and participate in fewer severe activities.
With 62.7% or 56.3%, respectively, facial fractures lead to severe head and soft-tissue damage. According to research, midface fractures increase the chance of brain damage, whereas facial fractures may potentially induce non-adjacent lesions.
What do we find?
According to the study, the nasal area (51.6%) is the most commonly affected by face fractures, followed by the midfacial and maxillofacial region (46%). It’s because of their obvious anatomic structure, increased vulnerability to external stress, and generally exposed nature. The majority of nasal fractures occur as a result of low-energy trauma, like aggression, assault, and a fall.
The midfacial area operates as the crumple zone, with zygoma fractures being the most prevalent (51.7%). Motorcycle accidents are associated with an 11-fold raise in the likelihood of maxillary fracture. Mandible fractures were much less common (n = 20, 15.9%) than in other face areas, presumably due to a lower prevalence of assault and fewer trauma from vehicle crashes and falls.
The frontal bone constitutes the toughest of the face bones and requires a great deal of power to fracture. When compared with the nasal as well as the midfacial regions, the occurrence of high-energy fractures was much lower, while orbital fractures significantly less common. According to our outcomes, social, environmental, and cultural factors all have a role in face fracture patterns.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, despite identical demographic features, patterns of face fractures may differ significantly because social, environmental, or cultural variables all play a role. The fact that the majority of foreigners in Bali choose motorbikes as their mode of transportation has resulted in a high number of MVAs. As a result, restrictions limiting their usage might be referred to as preventative.
Visit BIMC Hospital Kuta if you encounter an emergency situation which causes facial injury or more severe injuries. You easily schedule a Consultation with BIMC Hospital Kuta Plastic Surgeon for the best treatment for your injury. Our team will provide the best treatment for all your needs.